Financial Statements
Profit And Loss Account
Businesses need to produce financial statements to show how they are using the money invested in the business and if any of the investments have resulted in a return (profit). Financial statements are produced for the tax authorities, shareholders, investors and to satisfy legislation (company law). Financial Statements include Profit and Loss Accounts and Balance Sheets (Statement Of Financial Position), in this article we discuss what is a profit and loss account and how to compile a profit and loss account. We also provide an annotated profit and loss account.
What Is The Purpose Of A Profit And Loss Account?
A profit and loss account shows how much money the business has made (over the period that the accounts cover) and how much money it cost the business to do so. The profit and loss accounts cover an accounting period; usually one year. The profit and loss account is made up of three parts:
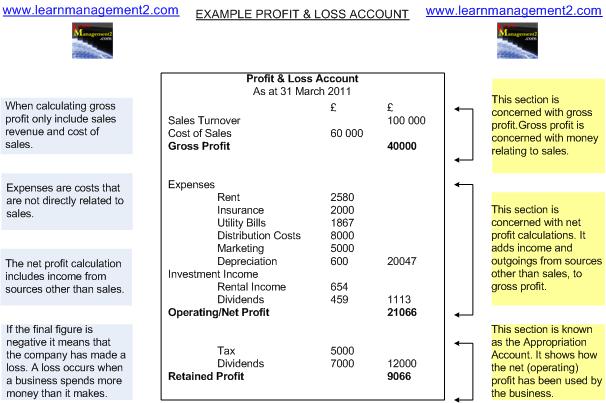
1. Gross Profit
This is the amount of money received from the sale of products (and/or services) minus the cost of sales. This figure only relates to goods sold in the accounting period that the profit and loss account covers. The gross profit section of the profit and loss account is known as the trade account as it covers trading activity. Gross profit does not cover overheads and expenses that do not relate directly to the production or purchase of goods.
Gross Profit = Sales Revenue MINUS Cost of Sales
2. Net Profit -
This section takes into account all of the money received by the business and all of expenses incurred by the business. Net profit is gross profit minus the expenses and income not included in the calculation for gross profit. It covers other income and expenses as the cost of sales and sales revenue were taken into account for the gross profit calculation.
Net Profit = Gross Profit MINUS Non Cost of Sale Expenses
PLUS Non Sales Income
In other words Net Profit = Total Revenue minus Total Expenses.
The net profit section of the accounts is known as profit and loss account as it shows all of the profit and loss made by the business.